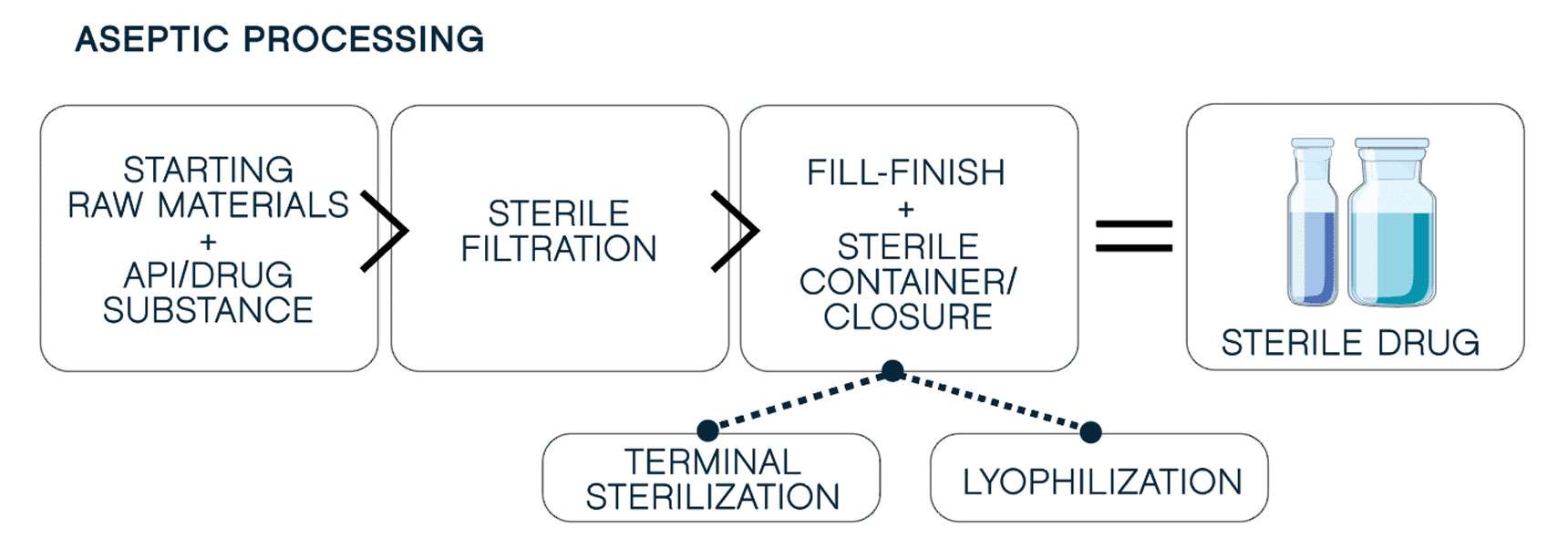
It starts with
analytical R&D, where experts develop and validate methods to confirm drug identity, purity, and potency, driving formulation development. Methods must be accurate and reproducible for seamless transfer to quality control labs—laying the groundwork for precise production.
Next, you must maintain quality at scale. Advanced machines make this possible, minimizing human intervention to reduce cross-contamination risk and ensure consistency. Robotic aseptic fill-finish meets the demands of the most complex formulations, including
oxygen-sensitive products. Our filling technology includes:
Through it all, you need to trust that your product is in safe hands—with a
GMP-certified partner who has mastered the regulatory maze. GMP standards dictate meticulous control and documentation of every detail, from air filtration to sterilization time limits, ensuring on-point aseptic product integrity.